What Is CAD Modeling? Types, Benefits & Software
At The Monster Builder, we combine CAD modeling with advanced manufacturing methods to turn your ideas into reality. Wether it’s cnc machining, sheet metal fabrication or 3D printing, CAD models are the digital backbone of every successful project.
What Is CAD Modeling?
CAD modeling (Computer-Aided Design modeling) is the process of creating precise 2D drawings or 3D digital models of parts, products, or systems using specialized software. It lets engineers design, test, and modify components virtually before manufacturing them through CNC machining, 3D printing, or injection molding.
- Think of it as a blueprint you can rotate and edit on your screen.
- These models show exact dimensions, tolerances, and materials.
- CAD helps engineers, designers, and manufacturers test and improve a design virtually, saving time and cost compared to physical prototypes.
How CAD Works
CAD (Computer-Aided Design) works by using specialized software to create and edit digital 2D drawings or 3D models of parts and assemblies. Designers start with sketches or 3D scans, then build precise models, run simulations, and export files (STEP, IGES, STL) to manufacturing processes like CNC machining, 3D printing, or injection molding.
Here’s the typical process:
- Start with a Concept or Scan: You can begin with a rough idea, a hand sketch, or even a 3D scan of an existing part. This information is imported into the CAD program.
- Build the 2D or 3D Model: Using CAD tools, you draw the shape of the part, adding holes, cutouts, bends, or curves. In 3D, you can spin, zoom, and measure every angle.
- Apply Materials and Properties: You assign materials (aluminium, steel, plastic) and thicknesses. The software then calculates weight, strength, and fit automatically.
- Test and Simulate: Many CAD programs let you run stress, flow, or motion analysis. This checks if the part can handle real-world loads before you manufacture it.
- Export the File for Manufacturin: When the design is ready, you save it in formats like STEP, IGES, or STL. These files go directly to machines for CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, plastic injection molding or 3D printing
- Make Adjustments Quickly: If something changes like a dimension, a hole location, a material, you update the CAD file. The new model is instantly ready for production.
In short, CAD turns ideas into a digital twin of your product, making it easier, faster, and safer to produce high-quality parts.

Types of CAD
There are five main types of CAD modeling: 2D Drafting, 3D Solid Modeling, Surface Modeling, Parametric Modeling, and Assembly Modeling. Each type serves a different purpose, from simple technical drawings to complex, parametric 3D designs used for CNC machining, sheet metal fabrication, and 3D printing.
2D Drafting
2D drafting creates flat, two-dimensional technical drawings. It’s used for floor plans, wiring diagrams, or sheet layouts where height/depth aren’t needed. In manufacturing, 2D drawings guide sheet metal fabrication, steel fabrication and basic part profiles before moving into 3D modeling.
3D Solid Modeling
Surface modeling produces complex curves and freeform surfaces without assigning volume. It’s used in industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods where smooth shapes, aerodynamics, or aesthetics matter. For example, modeling a car body or an ergonomic handle.
Parametric Modeling
Parametric modeling defines geometry with parameters, dimensions, and formulas. When a dimension changes, the entire model updates automatically. It’s used for parts that need frequent iteration, mass production, or design variations, such as plastic housings for injection molding or custom brackets for CNC machining.
Assembly Modeling
Assembly modeling lets designers combine multiple parts in one digital space. It’s used to check fit, movement, and interference between components before manufacturing. This prevents costly errors and helps plan assemblies for sheet metal or 3D printed parts.
Popular CAD Software
- AutoCAD – Industry standard for 2D drafting, widely used in architecture and engineering.
- SolidWorks – Parametric 3D modeling; ideal for mechanical and industrial products.
- Fusion 360 – Cloud-based CAD/CAM for start-ups and SMEs, integrates simulation and manufacturing.
- CATIA – High-end surfacing for aerospace and automotive industries.
- SketchUp – Quick conceptual 3D modeling for designers and architects.
For example, A product designer creates a prototype housing in Fusion 360, tests stress loads, then exports the file for FDM 3D printing to evaluate ergonomics before mass production.
Advantages of CAD Modeling
- Precision – Achieve millimetre-level accuracy for parts produced via CNC machining or plastic injection molding.
- Faster Prototyping – Quickly iterate and send models to SLA 3D printing or FDM 3D printing for functional testing.
- Cost Savings – Detect flaws digitally before making expensive tooling or molds
- Collaboration – Share files instantly with clients, suppliers, and fabricators.
- Automatic Documentation – Generate bills of materials (BOMs), exploded views, and drawings without extra work.
Not sure if your material will print well? Skim what materials cannot be used in 3D printing first before your CAD model will be production-ready from the start.
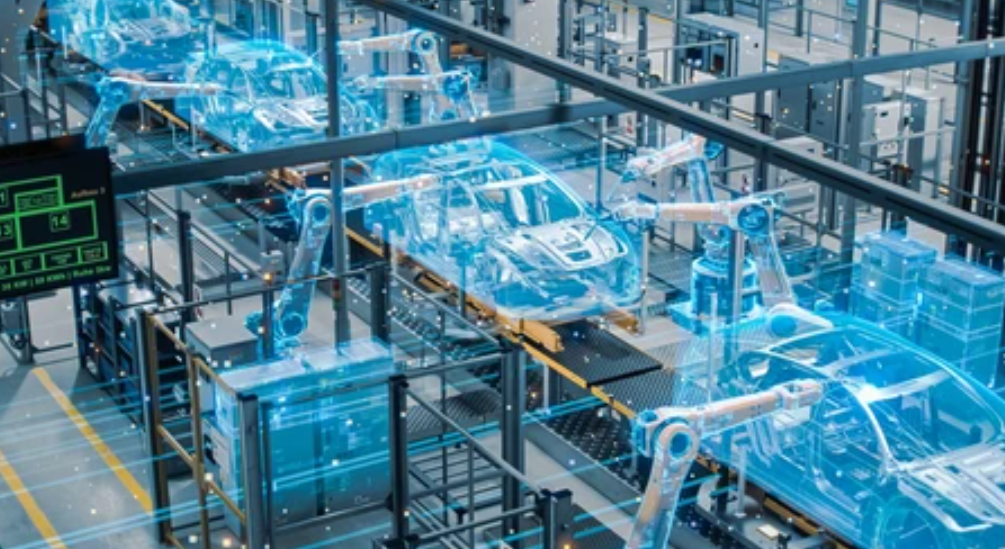

CAD Applications in Fabrication
CAD modeling supports nearly every service at The Monster Builder:
- CNC Machining Singapore – Import CAD models directly into CAM for high-precision parts.
- Aluminium Sheet Fabrication – Design flat layouts and bending sequences digitally.
- Plastic Injection Molding – Model molds and check for draft angles and undercuts.
- 3D Printing Singapore – Convert CAD to STL for SLA or FDM prototypes.
We take your CAD files (STEP, IGES, or Parasolid) and program them into our CNC machines. This is how we make precision parts for industries like automotive, marine, and electronics from engine brackets and custom housings to medical device components.
Conclusion
Whether you’re designing a simple bracket or a complex assembly, CAD modeling is the foundation of precise, efficient manufacturing. By working with The Monster Builder, you gain a partner who not only understands CAD but also knows how to turn your digital files into high-quality real-world parts. Our team in Singapore uses the latest software and manufacturing technologies from sheet metal fabrication to SLA and FDM 3D printing to help you move seamlessly from concept to finished product.
Contact The Monster Builder today to discuss your next project.



