Mold Manufacturing Process: How To Make A Mold
Looking for a clear guide to the mold manufacturing process in Singapore? Whether you’re developing a new product, scaling up production, or sourcing a reliable supplier, understanding how molds are designed, machined and validated can save you time, money and headaches.
What Is Mold Making?
Mold making is the process of creating a hollow form (called a mold) that shapes liquid or molten material such as plastic, metal or resin into a solid part with a specific design. It’s essential for manufacturing consistent, repeatable components in processes like plastic injection molding, die casting and composite forming.
In modern manufacturing, mold making involves CAD design, material selection, precision machining (like CNC milling and EDM) and rigorous testing. By creating an accurate mold, manufacturers can produce thousands of identical parts with high dimensional stability and lower per-unit cost.
Mold making bridges design, engineering, and fabrication. It demands precision, repeatability, and often strict tolerances.
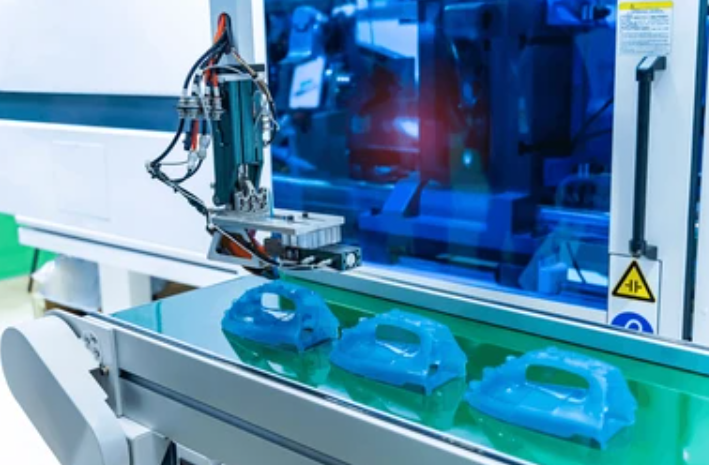

How Does Mold Making Work?
Here’s a step-by-step of the mold manufacturing process with current best practices:
- Design & Engineering (CAD Modeling): Engineers create a digital 3D model of the mold cavity and core.
- Material Selection: Choose tool steel, aluminium, silicone, or resin depending on volume, temperature, and cost.
- Prototype & Testing: Use 3D printing (SLA or FDM) or soft molds (urethane, silicone) to validate geometry, surface finish. Test small-batch prints to check shrinkage, warping, and functionality.
- Precision Machining: Cut the mold cavity using CNC milling and turning, achieve fine details with EDM, and refine surfaces via grinding and polishing.
- Assembly & Finishing: Fit inserts, add ejector pins, create cooling or heating channels, and apply coatings for wear resistance.
- Trial Runs & Quality Control: Test the mold in an injection molding machine or die-casting setup. Measure parts with CMM or 3D scanning to confirm tolerances and surface finish.
- Production: Once validated, the mold goes into full production. Regular maintenance extends mold life and ensures consistent parts.
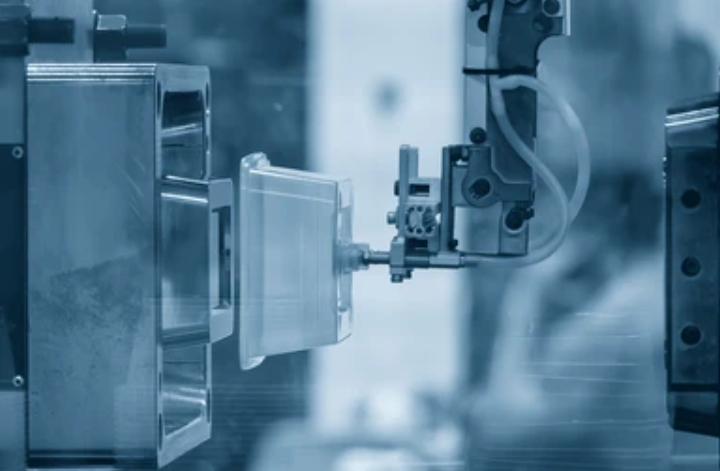
Equipment for Mold Manufacturing Process
Professional mold manufacturing process requires a combination of high-precision machines and inspection tools to produce durable, accurate molds for plastic injection molding, die casting, or prototype tooling. Below are the essential equipment and machines used in modern mold manufacturing:
- CNC Milling Machines (3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis) – For cutting complex mold cavities, cores, and inserts with high precision.
- CNC Lathes / Turning Centers – For producing round features, pins, bushings, and threaded inserts used inside molds.
- Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) – For cutting hard metals and creating fine details, sharp corners, and intricate slots.
- Sinker EDM – For deep cavities, undercuts, and areas unreachable by milling cutters.
- Surface Grinders and Cylindrical Grinders – For achieving tight tolerances, flat surfaces, and smooth finishes on mold plates.
- Polishing and Texturing Tools – For mirror finishes, gloss, or special textures on the mold cavity surface.
- Injection Molding Presses (for Trial Runs) – To test the mold under real process conditions before production.
- Quality Inspection Systems (CMM, Optical Measuring, 3D Scanning) – To verify dimensional accuracy, surface finish, and ensure parts meet tolerances.
- Cooling and Heating Channel Equipment – For creating integrated channels to control mold temperature and reduce cycle times.
- 3D Printers (SLA and FDM) – For rapid prototyping of mold inserts, patterns, or test fixtures before final machining.
During mold fabrication, precision drilling is essential for creating cooling channels, ejector pin holes and threaded inserts. Learn more in our guide on drilling machine types.

Supported Materials for Mold Making
Choosing the right material for your mold is critical for durability, cost, and performance. At The Monster Builder, we work with a wide range of mold-making materials to meet everything from rapid prototyping to high-volume production. Below are the most commonly supported materials:
- Tool Steel (H13, P20, S136, etc.) – Ideal for high-volume injection molds requiring strength, wear resistance and high-temperature performance.
- Pre-Hardened Steel – Easier to machine than hardened steel, making it suitable for medium-volume molds or when faster turnaround is needed.
- Aluminium (6061, 7075) – Lightweight, highly machinable, and perfect for low-volume molds, prototypes and rapid tooling with shorter lead times.
- Copper Alloys / Beryllium-Copper Inserts – Excellent thermal conductivity for faster cooling and reduced cycle times in plastic injection molding.
- Silicone Rubber – Flexible and affordable for casting small batches of resins, urethanes or low-temperature materials; good for prototyping and product testing.
- Epoxy or Urethane Resins – Low-cost molds for quick testing, prototyping, or decorative parts where high heat and pressure are not required.
- Hybrid Molds (Steel + Aluminium Inserts) – A cost-efficient approach combining steel’s durability with aluminium’s speed and weight advantages.
Material selection matters: tool steels and aluminium alloys vary in strength, hardness and ductility. Understanding ductility and why it’s important for mold-making materials can help you choose the best option for your application.
What Is the Best Material for Mold Making?
The best material for mold making depends on production volume, part requirements, and budget, but tool steel and aluminium are the most commonly used because they combine strength, precision and cost-effectiveness.
- Tool Steel (H13, P20, S136) – Best for high-volume production molds where durability, heat resistance, and wear resistance are critical.
- Aluminium (6061, 7075) – Best for low- to medium-volume molds, prototypes and rapid tooling because it’s lightweight and easy to machine.
- Silicone Rubber – Best for flexible, low-temperature molds or casting small batches of resin or urethane.
- Epoxy or Urethane Resins – Best for low-cost prototype molds where high heat or pressure isn’t required.
For many projects, a hybrid approach (steel mold base with aluminium inserts or copper cooling sections) gives the best balance of speed, cost, and lifespan.
What Is the Cheapest Material to Make a Mold?
The cheapest materials to make a mold are silicone rubber, epoxy resin and urethane resin because they are low-cost, easy to shape and ideal for small-batch or prototype production.
- Silicone Rubber – Flexible and inexpensive, perfect for low-temperature casting and short runs.
- Epoxy Resin – Affordable and quick to set, often used for prototype molds or decorative parts.
- Urethane Resin – Low-cost and versatile, suited for testing and low-pressure casting applications.
- Aluminium (for low-volume tooling) – Cheaper and faster to machine than hardened steel, a good option for small production runs.
While these materials are cheapest upfront, they have shorter lifespans than steel molds, making them more suitable for prototyping or limited production rather than high-volume manufacturing.
How Long Does Mold Making Typically Take?
Mold making typically takes anywhere from a few days to several weeks depending on the material, complexity and production volume.
- Prototype or resin molds – About 3–7 working days
- Aluminium or low-volume metal molds – Around 1–3 weeks
- Medium-complexity steel molds – Roughly 3–6 weeks
- High-complexity, multi-cavity hardened steel molds – 6–10+ weeks
How Much Does Mold Making Typically Cost?
Mold making typically costs between a few hundred and several thousand dollars depending on the mold size, material, complexity and production volume.
- Prototype or resin molds – About SGD 1,000–4,000 (quick, low-volume testing)
- Aluminium or low-volume molds – Around SGD 5,000–20,000 (short-run production)
- Hardened steel or high-volume molds – SGD 20,000–100,000+ (multi-cavity, complex parts)
Design complexity, cavity count, surface finish, cooling channels and coatings can all increase cost. Working with The Monster Builder which offers CNC machining, 3D printing, and plastic injection molding under one roof can lower your total project costs and reduce turnaround time.
Conclusion
Understanding the mold manufacturing process is key to producing high-quality, consistent parts at scale. By knowing how molds are designed, machined, and tested and by choosing the right materials, equipment, and timelines. You can significantly reduce defects, speed up production, and control costs.
At The Monster Builder, we combine CNC machining, 3D printing, and plastic injection molding under one roof. This integrated approach eliminates the need for multiple suppliers, shortens lead times, and ensures your molds and parts meet the highest quality standards. Interested? Contact us today!



