How Strong is 3D Printed Plastic?
Understanding how strong 3D printed plastic really is has become increasingly important as more Singapore businesses turn to additive manufacturing for prototypes and functional parts. Strength isn’t determined by just the material alone. Factors like design, printing orientation, and infill all play a major role. In this guide, we break down the actual strength of 3D printed plastics using real data, practical examples, and insights from our engineering experience at The Monster Builder.
If you want to understand how different printing technologies affect part durability, you can also read our FDM vs SLA comparison, where we break down accuracy, strength and application differences in detail.
Key Factors That Affect the Strength of 3D Printed Plastic
The strength of a 3D printed part is influenced by more than just the material itself. In real projects, especially functional prototypes or load-bearing components. Several engineering and printing factors work together to determine how strong and durable the final part becomes. Below are the most important factors you should consider when evaluating the strength of 3D printed plastic.
1. Material Type
Different plastics have different mechanical properties:
- PLA offers high tensile strength but is more brittle.
- ABS provides better impact resistance and flexibility.
- PETG balances toughness and strength, making it suitable for functional parts.
- Nylon delivers excellent durability and wear resistance.
Choosing the right material is the foundation of part strength.
2. Print Orientation
3D printed layers bond vertically, which means the part is strongest along the printed lines and weakest between the layers.
- A part printed standing upright may snap along its layers.
- The same part printed horizontally can withstand significantly more load.
- Proper orientation ensures the load is applied along the strongest axis.
3. Infill Density and Pattern
Infill determines the internal structure of your print:
- Higher infill (50–100%) increases strength.
- Infill patterns like grid, tri-hexagon, or gyroid distribute stress better than simple lines.
For functional parts, we often recommend a stronger internal structure, even if it increases print time.
4. Wall Thickness (Shells)
Walls contribute more to strength than infill.
- Thicker walls provide better rigidity.
- More perimeters improve impact resistance.
Most strong prints use 3–5 walls to support external loads.
5. Layer Height
Layer height affects how well each layer bonds:
- Smaller layer heights (0.1–0.2 mm) improve layer adhesion, increasing strength.
- Thicker layers print faster but reduce interlayer bonding.
For critical components, we typically choose finer layers for tighter bonding.
6. Print Temperature and Cooling
Correct temperature settings ensure good layer fusion:
- Too low, weak bonding, brittle layers
- Too high, stringing, loss of precision
- Controlled cooling prevents warping and cracks
Dialled-in temperature profiles directly influence part durability.
7. Post-Processing
Certain post-processing methods significantly improve strength:
- Annealing PLA increases heat resistance and tensile strength.
- Acetone smoothing strengthens ABS surface layers.
- Reinforcement with inserts (e.g., brass, steel) improves load-bearing areas.
These methods help parts perform better under stress.
8. Part Design
Good design practices make a major difference:
- Adding fillets to corners spreads the load evenly.
- Increasing ribbing improves structural stability.
- Avoiding unsupported thin walls prevents weak points.
Even small geometry adjustments can improve strength by 20–40%.
For parts that require high accuracy and smooth surface finish, SLA technology is often preferred. We also have a detailed guide comparing LCD, DLP, and SLA technologies to help you choose the right method for your project.

How Strong Is 3D Printed Plastic?
3D printed plastic can reach a tensile strength of around 50–70 MPa depending on the material, print orientation, and infill. PLA is strong in tension but more brittle, ABS offers better impact resistance, and PETG provides a good balance of strength and flexibility. A well-designed, properly printed part with 3–5 walls and 30–60% infill can be strong enough for functional prototypes, brackets, fixtures, and load-bearing components. Strength increases further through better orientation, higher temperature bonding, and post-processing like annealing.
How Strong Is PLA (Polylactic Acid)?
PLA is one of the most commonly used filaments for 3D printing, especially for prototyping. PLA has a tensile strength of about 50–70 MPa, making it one of the strongest standard 3D printing plastics in terms of tensile performance. It offers high rigidity and good dimensional accuracy, but it is more brittle compared to materials like ABS or PETG. PLA performs best in applications that require strength under steady loads but not heavy impact or high heat. With proper print orientation, 3–5 wall perimeters, and 20–60% infill, PLA parts can be strong enough for brackets, tools, fixtures, and functional prototypes.
PLA behaves differently depending on its formulation and manufacturing process. You can learn more about how PLA is produced and why it’s considered a more sustainable 3D printing material in our material guide.
For applications in warm environments (e.g., under-the-hood, near electronics), or parts exposed to heat, standard PLA may deform. In those cases, consider other materials or reinforced PLA.
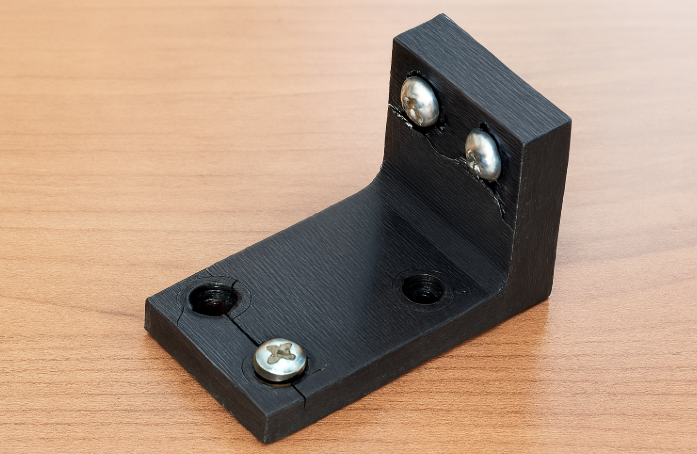
Real-World Example: PLA Part Holding Weight
To show how strong PLA can be in practical use, here’s a real example from a test carried out by our team at The Monster Builder. We printed a load-bearing hook using standard PLA, designed with 5 wall perimeters and 30% infill. The part was tested in different print orientations to measure how much weight each configuration could support.
In the side-down orientation, which aligned the layers with the load direction, the PLA hook was able to hold over 120 kg before it finally failed.
This demonstrates that with the right design, print orientation, and structural settings, even standard PLA can handle unexpectedly high loads, making it suitable for brackets, fixtures, and functional prototypes.
How to Improve the Strength of 3D Printed Plastic
At The Monster Builder, our strength-optimised 3D printing process focuses on engineering principles, correct material behaviour, and controlled printing parameters. Below are the main techniques we use to ensure your 3D printed parts are strong, reliable, and suitable for functional use.
1. Increase Infill Percentage for Strong Internal Support
A higher infill percentage makes the internal structure of the part denser and more resistant to bending or compression.
How we do it:
- Functional parts: 40–80% infill
- Load-bearing components: up to 100% infill
- Gyroid or cubic infill to distribute stress evenly
For example, a PLA hinge printed at 20% infill bent easily during testing, but the same hinge printed at 60% infill held its shape and supported repeated opening/closing cycles.
2. Optimise Wall Thickness (Shells) for Better Load Distribution
Walls (outer perimeters) provide most of a part’s durability. Adding more walls increases impact resistance and stiffness.
How we do it:
- Standard parts: 3 walls
- High-strength parts: 4–6 walls
- Important mounting areas reinforced with thicker shells
For example, a mounting bracket printed with only 2 walls cracked around the screw holes. With 5 walls, the bracket supported the weight of a small motor without deformation.
3. Control Print Orientation to Maximise Layer Strength
3D printed parts are weakest between layers. By rotating the model, we ensure the load is supported along the strongest axis.
How we do it:
- Print long parts horizontally to avoid vertical delamination
- Align hooks, arms, and brackets so the force runs parallel to the layers
- Analyse load direction and adjust orientation accordingly
For example, a PLA hook printed upright broke at 15 kg. Rotated sideways (layers aligned with force), the same hook held over 100 kg.
4. Apply Post-Processing to Strengthen Material Bonds
Post-processing methods enhance layer bonding, temperature resistance, and overall part strength.
How we do it:
- Annealing PLA to relieve internal stresses and increase heat resistance
- Controlled heating & slow cooling to reduce brittleness
- Finishing surfaces to reduce stress points
Example:
An annealed PLA gear printed by our team withstood 30–40% higher torque compared to a non-annealed version.
5. Reinforce Parts Using Stronger Materials or Hardware
Some applications require extra reinforcement beyond typical PLA strength.
How we do it:
- Composite filaments (carbon-fibre PLA, nylon blends) for high strength
- Metal inserts (brass, stainless steel) to strengthen screw connections
- Hybrid assemblies that combine printed parts with metal fasteners
Example:
A client needed a high-strength fixture. By adding brass threaded inserts and switching to carbon-fibre PLA, the fixture handled daily industrial use without wear.
3D Printed Parts Supplier in Singapore
3D printed plastic can be incredibly strong when the right material, print settings, and design principles are used. From tensile strength to impact resistance, factors like infill, wall thickness, orientation, and post-processing all play a major role in how durable a printed part becomes. With proper optimisation, even standard PLA can handle impressive loads and perform reliably in real-world applications.
At The Monster Builder, we combine engineering expertise with advanced FDM 3D printing and SLA 3D printing technologies to deliver high-strength, high-accuracy parts for clients across Singapore. Whether you’re building functional prototypes, fixtures, brackets, or end-use components, our team ensures every part is designed and printed for maximum strength and performance.
If you need reliable 3D printed parts in Singapore, we’re here to help you choose the right material, printing method, and structural setup to achieve the results you want quickly, accurately, and with quality you can trust.